1
Dispatch → Account → Other
Russian Federation Overview

.
RUSSIAN FEDERATION
Russia (Russian: Россия, Rossiya), or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world by area, covering over 17 million square kilometres and encompassing more than one-eighth of Earth's inhabited land area. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has the most borders of any country in the world, with sixteen sovereign nations. It has a population of 143.7 million; and is the most populous country in Europe, and the ninth-most populous country in the world. Moscow, the capital, is the largest city in Europe, while Saint Petersburg is the nation's second-largest city and cultural centre. Russians are the largest Slavic and European nation; they speak Russian, the most spoken Slavic language, and the most spoken native language in Europe.

Flag

Location
Population: 146,171,015
-Density: 8.5/km²
Capital: Moscow
Largest City: Moscow
Official Language: Russian
National Language:
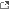 See languages of Russia
See languages of Russia Demonym: Russian
Government:
• President: Vladimir Putin
• Prime Minister: Mikhail Mishustin
• Speaker of the Federation Council: Valentina Matviyenko
• Speaker of the State Duma: Vyacheslav Volodin
• Chief Justice: Vyacheslav Lebedev
Legislature:
- Upper House: Federation Council
-Lower House: State Duma
Formation:
• Rurikids founded: 862
• Kievan Rus': 879
• Duchy of Moscow: 1283
• Tsardom of Russia: 16 January 1547
• Russian Empire: 2 November 1721
• Monarchy abolished: 15 March 1917
• Soviet Union: 30 December 1922
• Russian Federation: 12 December 1991
• Current constitution: 12 December 1993
• Last polity admitted: 18 March 2014
• Last amendments: 4 July 2020
Land Area: 17,098,246 km²
Water %: 13
Elevation
Highest Point: Mount Elbrus 5,642 m
Lowest Point: Caspian Sea, −28 m
GDP (nominal): $ 1.745 trillions
GDP (nominal) per capita: $ 11.405
Human Development Index: 0.824
Currency: Russian Ruble (₽)(RUB)
Time Zone: UTC +2 to +12
Drives on the: right
Calling code: +7
Internet TLD: .ru .рф
RUSSIAN FEDERATION
The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD. The medieval state of Rus' arose in the 9th century. In 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire, beginning the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures that defined Russian culture for the next millennium. Rus' ultimately disintegrated until it was finally reunified by the Grand Duchy of Moscow in the 15th century. By the 18th century, the nation had greatly expanded through conquest, annexation, and exploration to become the Russian Empire, the third-largest empire in history. Following the Russian Revolution, the Russian SFSR became the largest and leading constituent of the Soviet Union, the world's first constitutionally socialist state, which had a one-party system throughout most of its existence. The Soviet Union played a decisive role in the Allied victory in World War II, and emerged as a superpower and rival to the United States during the Cold War. The Soviet era saw some of the most significant technological achievements of the 20th century, including the world's first human-made satellite and the launching of the first human in space. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Russian SFSR reconstituted itself as the Russian Federation. In the aftermath of the constitutional crisis of 1993, a new constitution was adopted, and Russia has since been governed as a federal semi-presidential republic. Vladimir Putin has dominated Russia's political system since 2000, and his government has been accused of authoritarianism, numerous human rights abuses, and corruption.
Russia is a great power, and is considered a potential superpower. It is ranked 52nd in the Human Development Index, with a universal healthcare system, and a free university education. Russia's economy is the world's eleventh-largest by nominal GDP and the sixth-largest by PPP. It is a recognised nuclear-weapons state, possessing the world's largest stockpile of nuclear weapons, with the world's second-most powerful military, and the fourth-highest military expenditure. Russia's extensive mineral and energy resources are the world's largest, and it is one of the leading producers of oil and natural gas globally. It is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, a member of the G20, the SCO, the Council of Europe, the APEC, the OSCE, the IIB and the WTO, as well as the leading member of the CIS, the CSTO, and the EAEU. Russia is also home to the ninth-greatest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
1 Etymology
2 History
3 Geography
4 Government
4.1 Foreign Relations and Military
5 Economy
6 Culture
7 Infrastructure
7.1 Energy
The name Russia is derived from Rus', a medieval state populated primarily by the East Slavs. However, the proper name became more prominent in later history, and the country typically was called by its inhabitants "Русская земля" (Russkaya zemlya), which can be translated as "Russian land". In order to distinguish this state from other states derived from it, it is denoted as Kievan Rus' by modern historiography. The name Rus' itself comes from the early medieval Rus' people, a group of Norse merchants and warriors who relocated from across the Baltic Sea and founded a state centred on Novgorod that later became Kievan Rus'.
A Medieval Latin version of the name Rus' was Ruthenia, which was used as one of several designations for East Slavic and Eastern Orthodox regions, and commonly as a designation for the lands of Rus'. The current name of the country, Россия (Rossiya), comes from the Byzantine Greek designation of the Rus', Ρωσσία Rossía—spelled Ρωσία (Rosía pronounced [roˈsia]) in Modern Greek.
The standard way to refer to the citizens of Russia is "Russians" in English. There are two words in Russian which are commonly translated into English as "Russians"—one is "русские" (russkiye), which most often refers to ethnic Russians—and the other is "россияне" (rossiyane), which refers to citizens of Russia, regardless of ethnicity.
Russia is a transcontinental country stretching vastly over both Europe and Asia. Russia's border neighbors are Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Byeloruthenia, Ukraine, Georgia, Persia, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia and Korea. It spans the northernmost corner of Eurasia, and has the world's fourth-longest coastline, at 37,653 km. Russia lies between latitudes 41° and 82° N, and longitudes 19° E and 169° W, and is larger than three continents: Oceania, Europe, and Antarctica, while having the same surface area as Pluto.
Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's westernmost part along the Baltic Sea, is about 9,000 km apart from its easternmost part, Big Diomede Island in the Bering Strait. Russia has nine major mountain ranges, and they are found along the southern regions, which share a significant portion of the Caucasus Mountains (containing Mount Elbrus, which at 5,642 m is the highest peak in Russia and Europe); the Altai and Sayan Mountains in Siberia; and in the East Siberian Mountains and the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Russian Far East (containing Klyuchevskaya Sopka, which at 4,750 m is the highest active volcano in Eurasia). The Ural Mountains, running north to south through the country's west, are rich in mineral resources, and form the traditional boundary between Europe and Asia.
Russia borders three, oceans, when including its links with over thirteen marginal seas. Russia's major islands and archipelagos include Novaya Zemlya, Franz Josef Land, Severnaya Zemlya, the New Siberian Islands, Wrangel Island, the Kuril Islands, and Sakhalin. The Diomede Islands are just 3.8 km apart, and Kunashir Island is just 20 km from Hokkaido, Japan.
Russia, home to over 100,000 rivers, has one of the world's largest surface water resources, with its lakes containing approximately one-quarter of the world's liquid fresh water. Lake Baikal, the largest and most prominent among Russia's fresh water bodies, is the world's deepest, purest, oldest and most capacious fresh water lake, containing over one-fifth of the world's fresh surface water. Ladoga and Onega in northwestern Russia are two of the largest lakes in Europe. Russia is second only to Brazil by total renewable water resources. The Volga, widely seen as Russia's national river due to its historical importance, is the longest river in Europe. The Siberian rivers of Ob, Yenisey, Lena and Amur are among the world's longest rivers.
Climate
The sheer size of Russia and the remoteness of many areas from the sea result in the dominance of the humid continental climate, which is prevalent in all parts of the country except for the tundra and the extreme southwest. Mountains in the south and east obstruct the flow of warm air masses from the Indian and Pacific oceans, while the plain of the west and north makes the country open to Arctic and Atlantic influences. Most of Northwest Russia and Siberia has a subarctic climate, with extremely severe winters in the inner regions of Northeast Siberia (mostly Sakha, where the Northern Pole of Cold is located with the record low temperature of −71.2 °C or −96.2 °F), and more moderate winters elsewhere. Russia's vast stretch of land along the Arctic Ocean and the Russian Arctic islands have a polar climate.
The coastal part of Krasnodar Krai on the Black Sea, most notably Sochi, and some coastal and interior strips of the North Caucasus possess a humid subtropical climate with mild and wet winters. In many regions of East Siberia and the Russian Far East, winter is dry compared to summer; while other parts of the country experience more even precipitation across seasons. Winter precipitation in most parts of the country usually falls as snow. The westernmost parts of Kaliningrad Oblast on the Vistula Spit, and some parts in the south of Krasnodar Krai and the North Caucasus have an oceanic climate. The region along the Lower Volga and Caspian Sea coast, as well as some southernmost silvers of Siberia, possess a semi-arid climate.
Throughout much of the territory, there are only two distinct seasons—winter and summer—as spring and autumn are usually brief periods of change between extremely low and extremely high temperatures. The coldest month is January (February on the coastline); the warmest is usually July. Great ranges of temperature are typical. In winter, temperatures get colder both from south to north and from west to east. Summers can be quite hot, even in Siberia.
Biodiversity
Russia, owing to its gigantic size, has diverse ecosystems, including polar deserts, tundra, forest tundra, taiga, mixed and broadleaf forest, forest steppe, steppe, semi-desert, and subtropics.[184] About half of Russia's territory is forested,[5] and it has the world's largest forest reserves, which are known as the "Lungs of Europe"; coming second only to the Amazon rainforest in the amount of carbon dioxide it absorbs.[186]
Russian biodiversity includes 12,500 species of vascular plants, 2,200 species of bryophytes, about 3,000 species of lichens, 7,000-9,000 species of algae, and 20,000-25,000 species of fungi. Russian fauna is composed of 320 species of mammals, over 732 species of birds, 75 species of reptiles, about 30 species of amphibians, 343 species of freshwater fish (high endemism), approximately 1,500 species of saltwater fishes, 9 species of cyclostomata, and approximately 100–150,000 invertebrates (high endemism). Approximately 1,100 of rare and endangered plant and animal species are included in the Russian Red Data Book.
Russia's entirely natural ecosystems are conserved in nearly 15,000 specially protected natural territories of various statuses, occupying more than 10% of the country's total area. They include 45 UNESCO biosphere reserves, 64 national parks, and 101 nature reserves. Russia still has many ecosystems which are still untouched by man—mainly in the northern taiga areas and the subarctic tundra of Siberia. Over time the country has been having improvement and application of environmental legislation, development and implementation of various federal and regional strategies and programmes, and study, inventory and protection of rare and endangered plants, animals, and other organisms, and including them in the Russian Red Data Book.
According to the Constitution of Russia, the country is an asymmetric federation and semi-presidential republic, wherein the president is the head of state, and the prime minister is the head of government. The Russian Federation is fundamentally structured as a multi-party representative democracy, with the federal government composed of three branches:
Legislative: The bicameral Federal Assembly of Russia, made up of the 450-member State Duma and the 170-member Federation Council, adopts federal law, declares war, approves treaties, has the power of the purse and the power of impeachment of the president.
Executive: The president is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces, can veto legislative bills before they become law, and appoints the Government of Russia (Cabinet) and other officers, who administer and enforce federal laws and policies.
Judiciary: The Constitutional Court, Supreme Court and lower federal courts, whose judges are appointed by the Federation Council on the recommendation of the president, interpret laws and can overturn laws they deem unconstitutional.
The president is elected by popular vote for a six-year term (eligible for a second term, but not for a third consecutive term). Ministries of the government are composed of the premier and his deputies, ministers, and selected other individuals; all are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister (whereas the appointment of the latter requires the consent of the State Duma).
Foreign Relations and Military
Diplomacy
As of 2019, Russia has the fifth-largest diplomatic network in the world; maintaining diplomatic relations with 190 United Nations member states, two partially-recognized states, and three United Nations observer states; with 144 embassies. It is considered a potential superpower; and is a historical great power, an important regional power, and one of five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council. Russia is a member of the G20, the Council of Europe, the OSCE, and the APEC, and takes a leading role in organisations such as the CIS, the EAEU andthe CSTO.
Russia maintains positive relations with other countries of EAEU, especially with neighbouring Byeloruthenia, which is in the Union State, a supranational confederation of the latter with Russia. Serbia has been a historically close ally of Russia since centuries, as both countries share a strong mutual cultural, ethnic, and religious affinity. In the 21st century, Sino-Russian relations have significantly strengthened bilaterally and economically—the Treaty of Friendship, and the construction of the ESPO oil pipeline and the Power of Siberia gas pipeline formed a special relationship between the two. India is the largest customer of Russian military equipment, and the two countries share a historically strong strategic and diplomatic relationship since the Soviet times.
Russian Armed Forces
The Russian Armed Forces are divided into the Ground Forces, the Navy, and the Aerospace Forces—and there are also two independent arms of service: the Strategic Missile Troops and the Airborne Troops. As of 2019, the military had around one million active-duty personnel, which is the world's fourth-largest. Additionally, there are over 2.5 million reservists, with the total number of reserve troops possibly being as high as 20 million. It is mandatory for all male citizens aged 18–27 to be drafted for a year of service in Armed Forces.
Russia boasts the world's second-most powerful military, and is among the five recognised nuclear-weapons states, with the world's largest stockpile of nuclear weapons. More than half of the world's 13,500 nuclear weapons are owned by Russia. The country possesses the second-largest fleet of ballistic missile submarines, and is one of the only three states operating strategic bombers, with the world's most powerful ground force, the second-most powerful air force, and the third-most powerful navy fleet. Russia has the world's fourth-highest military expenditure, spending $65.1 billion in 2019. It has a large and fully indigenous arms industry, producing most of its own military equipment, and is the world's second-largest exporter of arms, behind only the United States.
Railway transport in Russia is mostly under the control of the state-run Russian Railways. The total length of common-used railway tracks is the world's third-longest, and exceeds 87,157 km. As of 2016, Russia has 1,452.2 thousand km of roads, and its road density is among the world's lowest. Russia's inland waterways are the world's second-longest, and total 102,000 km. Among Russia's 1,218 airports, the busiest is Sheremetyevo International Airport in Moscow, which is also the fifth-busiest airport in Europe.
Russia's largest port is the Port of Novorossiysk in Krasnodar Krai along the Black Sea. It is the world's sole country to operate nuclear-powered icebreakers, which advance the economic exploitation of the Arctic continental shelf of Russia, and the development of sea trade through the Northern Sea Route.
Russia has been widely described as an energy superpower; as it has the world's largest natural gas reserves, the second-largest coal reserves, the eighth-largest oil reserves, and the largest oil shale reserves in Europe. It is the world's leading natural gas exporter, the second-largest natural gas producer, and the second-largest oil exporter, and producer. Fossil fuels cause most of the greenhouse gas emissions by Russia. The country is the world's fourth-largest electricity producer, and the ninth-largest renewable energy producer in 2019. Russia was also the world's first country to develop civilian nuclear power, and to construct the world's first nuclear power plant. In 2019, It was the world's fourth-largest nuclear energy producer.
All Rights Reserved © Ministry of Culture | Government of the Russian Federation









